cURL
To restore a Droplet from a backup with cURL, call:
# Enable Backups
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"enable_backups"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Disable Backups
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"disable_backups"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Reboot a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"reboot"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Power cycle a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"power_cycle"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Shutdown and Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"shutdown"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3067649/actions"
# Power off a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"power_off"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Power on a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"power_on"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
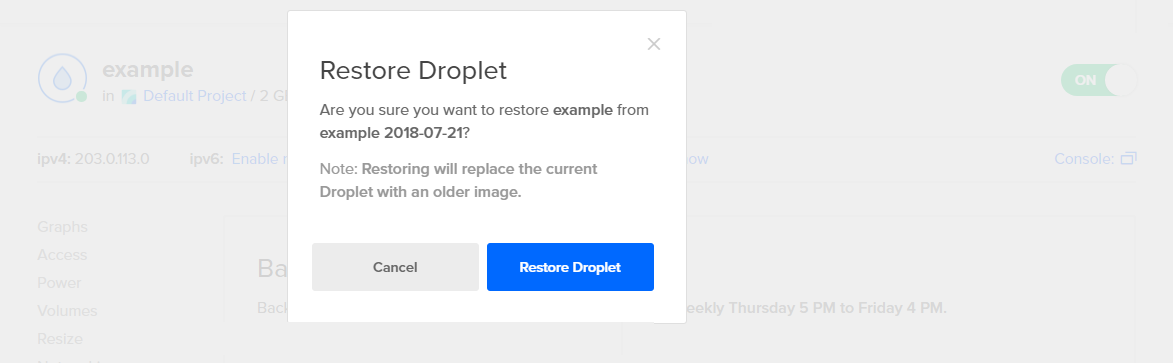
# Restore a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"restore", "image": 12389723 }' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3067649/actions"
# Password Reset a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"password_reset"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Resize a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"resize","size":"1gb"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Rebuild a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"rebuild","image":"ubuntu-16-04-x64"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Rename a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"rename","name":"nifty-new-name"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Change the Kernel
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"change_kernel","kernel":991}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Enable IPv6
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"enable_ipv6"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Enable Private Networking
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"enable_private_networking"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Snapshot a Droplet
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"snapshot","name":"Nifty New Snapshot"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164450/actions"
# Acting on Tagged Droplets
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"enable_backups"}' \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/actions?tag_name=awesome"
# Retrieve a Droplet Action
curl -X GET \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN" \
"https://api.digitalocean.com/v2/droplets/3164444/actions/36804807"
Go
Go developers can use Godo,
the official DigitalOcean V2 API client for Go. To restore a Droplet from a backup with Godo, use the
following code:
import (
"context"
"os"
"github.com/digitalocean/godo"
)
func main() {
token := os.Getenv("DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN")
client := godo.NewFromToken(token)
ctx := context.TODO()
// Enable Backups
action, _, err := client.DropletActions.EnableBackups(ctx, 3164450)
// Disable Backups
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.DisableBackups(ctx, 3164450)
// Reboot a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Reboot(ctx, 3164450)
// Power Cycle a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.PowerCycle(ctx, 3164450)
// Shutdown a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Shutdown(ctx, 3067649)
// Power Off a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.PowerOff(ctx, 3164450)
// Power On a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.PowerOn(ctx, 3164450)
// Restore a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Restore(ctx, 3164449, 12389723)
// Password Reset a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.PasswordReset(ctx, 3164450)
// Resize a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Resize(ctx, 3164450, "1gb", true)
// Rebuild a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.RebuildByImageSlug(ctx, 3164450, "ubuntu-16-04-x64")
// Rename a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Rename(ctx, 3164450, "nifty-new-name")
// Change the Kernel
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.ChangeKernel(ctx, 3164450, 991)
// Enable IPv6
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.EnableIPv6(ctx, 3164450)
// Enable Private Networking
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.EnablePrivateNetworking(ctx, 3164450)
// Snapshot a Droplet
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Snapshot(ctx, 3164450, "Nifty New Snapshot")
// Retrieve a Droplet Action
// action, _, err := client.DropletActions.Get(ctx, 3164450, 36804807)
}
Ruby
Ruby developers can use DropletKit,
the official DigitalOcean V2 API client for Ruby. To restore a Droplet from a backup with DropletKit, use the
following code:
require 'droplet_kit'
token = ENV['DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN']
client = DropletKit::Client.new(access_token: token)
# Enable Backups
client.droplet_actions.enable_backups(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Disable Backups
# client.droplet_actions.disable_backups(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Reboot a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.reboot(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Power Cycle a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.power_cycle(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Shutdown a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.shutdown(droplet_id: 3067649)
# Power Off a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.power_off(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Power On a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.power_on(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Restore a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.restore(droplet_id: 3067649, image: 12389723)
# Password Reset a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.password_reset(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Resize a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.resize(droplet_id: 3164450, size: '1gb')
# Rebuild a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.rebuild(droplet_id: 3164450, image: 'ubuntu-16-04-x64')
# Rename a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.rename(droplet_id: 3164450, name: 'nifty-new-name')
# Change the Kernel
# client.droplet_actions.change_kernel(droplet_id: 3164450, kernel: 991)
# Enable IPv6
# client.droplet_actions.enable_ipv6(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Enable Private Networking
# client.droplet_actions.enable_private_networking(droplet_id: 3164450)
# Snapshot a Droplet
# client.droplet_actions.snapshot(droplet_id: 3164450, name: 'Nifty New Snapshot')
Python
import os
from pydo import Client
client = Client(token=os.environ.get("DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN"))
# enable back ups example
req = {
"type": "enable_backups"
}
resp = client.droplet_actions.post(droplet_id=346652, body=req)