
Machines are high-performing computing for scaling AI applications.
Use our IPSec VPN tunnels to connect to your Private Network from your office or third-party site. VPN Gateways can be attached to your Private Network, establishing a site-to-site VPN tunnel. This enables two-way communication between your Paperspace machines and devices in your office or third-party site.
This feature can be added anytime by clicking the VPN tab in the console.
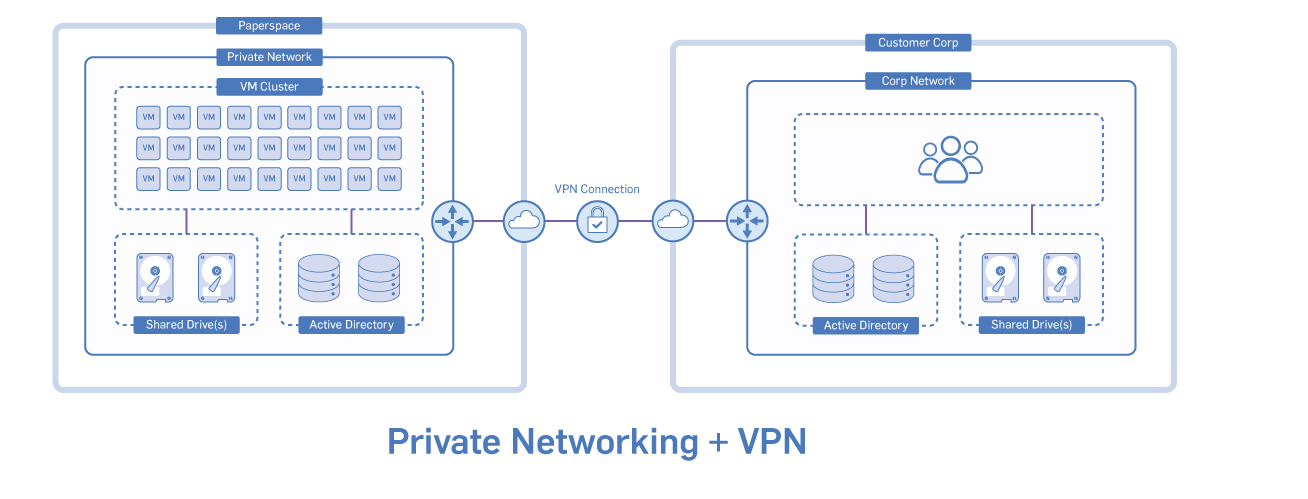
Paperspace site-to-site VPN Gateways leverage the Internet Protocol security (IPsec) protocol.
A Private Network is required in order to provision a VPN Gateway. The VPN Gateway is added to this Private Network.
Supply the following parameters when configuring your side of the VPN tunnel:
The Gateway IP (the tunnel endpoint on the Paperspace side) is specific to your Region. West Region: 64.62.255.10 East Region: 184.105.3.10 Europe: 74.82.28.10
The subnet of your Paperspace Private Network is listed under the Network tab of the console in CIDR format, for example 10.30.254.0/24.
Recommended: IKEv2 Fallback: IKEv1
Recommended: AES256 (AES256-CBC), SHA2 (SHA256) Fallback: AES128, SHA1, MD5
Not supported: DES, 3DES, SHA256-96 AES256-GCM
Recommended: 14 Fallback: 2, 5, 15-18, 22, 23, 24
Key life is the time each tunnel takes until it regenerates a new renegotiated key pair. This is performed to maintain the highest security between the two tunnels. While generally, key life need not match between tunnel endpoints, setting your key lifetimes to the below guarantees smooth operation and prevents the possibility of premature tunnel tear-downs.
Phase 1: 10800 seconds
Phase 2: 3600 seconds
Please white list the respective Paperspace Gateway IP allowing it connections on UDP ports 500 and 4500.
Each IPSEC tunnel endpoint has a unique identifier. In most cases, this is automatically set to be the same as the actual tunnel endpoint IP address. However, there exist scenarios where this may not be the case (detailed below). In such a case you are required to specify a “Local ID” for your IPSEC tunnel. Please set this ID by hand to match the external (Internet IP address) of your end of the tunnel. When in doubt, set a “Local ID” by hand.
The cases where one might be required to perform this are:
This can be set on most devices by specifying “LocalID” (sometimes called “ID”), typically found under the authentication portion of the configuration.
PROMPT> ping 10.0.0.3 Pinging 10.0.0.3 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.0.0.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 10.0.0.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 10.0.0.3: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 10.0.0.3:
Packets: Sent = 3, Received = 3, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milliseconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms